The Role of FWC Officers: Powers and Limitations
Florida, a state renowned for its rich biodiversity, is a haven for nature enthusiasts. Ensuring the protection of its ecological wonders are the dedicated FWC officers. But who exactly are these officers, and what boundaries define their authority? This article aims to elucidate the intricate balance of power and responsibility vested in these guardians of nature.
The Genesis of FWC Officers
The Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) recognized the need for a specialized force that could straddle the realms of law enforcement and environmental conservation. Thus, the FWC officers were born. Rigorously trained, they are equipped to tackle challenges ranging from illegal hunting to public safety in wildlife-rich zones.
The Multifaceted Powers of FWC Officers
Broad Jurisdiction: FWC officers are not limited to wildlife reserves or protected areas. Their jurisdiction spans the entirety of Florida, from its dense forests to its bustling urban centers. This wide reach ensures comprehensive enforcement of wildlife regulations.
Diverse Enforcement: Beyond the realm of wildlife, FWC officers are empowered to enforce boating safety regulations, environmental protection laws, and even some federal statutes. This diverse mandate ensures that all facets of Florida’s ecological well-being are safeguarded.
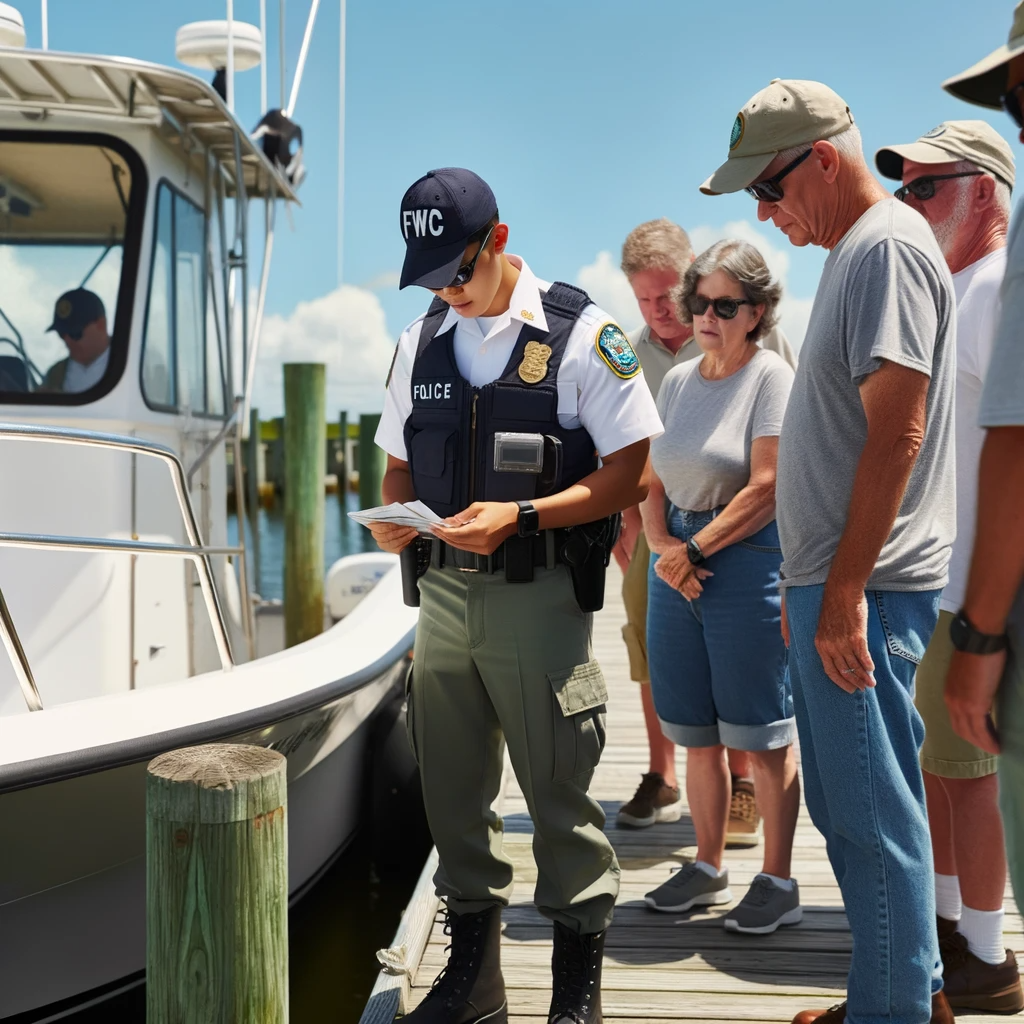
Inspection Rights: Whether it’s a serene day on a Floridian lake or a bustling fish market, FWC officers have the authority to inspect vessels, fishing gear, catches, and commercial establishments. These inspections, rooted in legal mandates, ensure adherence to conservation goals.
The Inherent Limitations
Constitutional Respect: While FWC officers wield significant power, they are bound by the Constitution. Every search, seizure, or arrest is conducted with respect for individual rights and due process.
Jurisdictional Boundaries: Despite their broad reach, there are areas and situations outside the purview of FWC officers. They operate within specific legal confines, ensuring their actions are always justifiable.
Public Interaction Protocols: Every interaction between an FWC officer and a member of the public is governed by established protocols. These guidelines ensure that while officers fulfill their duties, the rights and dignity of individuals remain paramount.
The Symbiotic Relationship with the Public
Understanding the role of FWC officers is not just about knowing the rules; it’s about fostering a collaborative spirit. Officers often engage in public awareness campaigns, educating Floridians about wildlife laws, and the importance of conservation. Their approach is rooted in mutual respect and a shared love for Florida’s natural heritage.
Real-world Interactions
Consider Mark, a fisherman who was recently approached by an FWC officer. The officer, after a brief introduction, inspected Mark’s catch, ensuring it adhered to size and species regulations. Mark, aware of the officer’s authority, cooperated fully. This cordial interaction is a testament to the harmonious relationship achievable between the public and FWC officers.
The Road Ahead
As Florida grapples with the challenges of urbanization and climate change, the role of FWC officers becomes even more pivotal. They stand as the first line of defense against ecological degradation, ensuring that future generations inherit a Florida as pristine as we did.
FWC officers, with their unique blend of authority and responsibility, are the unsung heroes of Florida’s conservation narrative. As we navigate the intricate web of wildlife laws, it’s reassuring to know that these dedicated officers are on the frontlines, protecting our state’s ecological legacy. If you or someone you know requires guidance on FWC regulations or faces potential violations, don’t hesitate. Reach out to Sando Law for expert advice today!
Sando Law, P.A. represents clients pre and post criminal charges, clients facing fish and wildlife violations, and clients in need of immigration counsel.